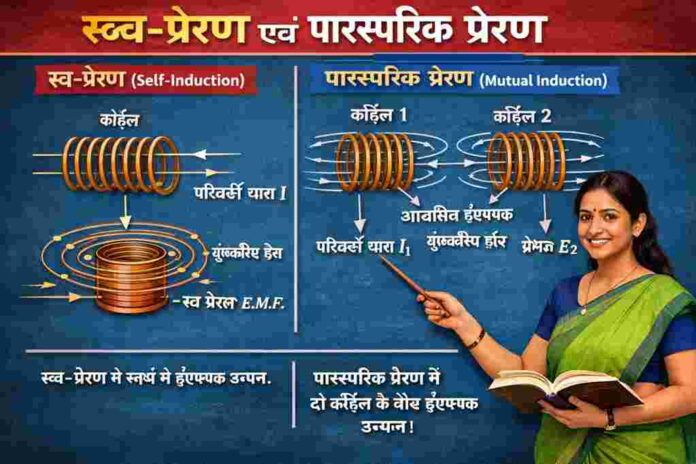
Self and Mutual Induction (स्व–प्रेरण एवं पारस्परिक प्रेरण) विद्युतचुंबकत्व (Electromagnetism) भौतिकी का एक अत्यंत महत्वपूर्ण भाग है। जब किसी कुंडली (Coil) में बहने वाली धारा बदलती है, तो वह स्वयं में या पास की दूसरी कुंडली में EMF (विद्युत वाहक बल) उत्पन्न कर सकती है।
इसी प्रक्रिया को दो भागों में समझा जाता है:
👉 Self Induction (स्व–प्रेरण)
👉 Mutual Induction (पारस्परिक प्रेरण)
UP Board Class 12 में यह टॉपिक बहुत scoring माना जाता है क्योंकि इससे अक्सर numerical + derivation + definition पूछी जाती है।
इस अध्याय को यदि आप concept से समझ लेते हैं, तो Electromagnetic Induction का पूरा भाग आसान हो जाता है।
🔷 What is Induction? (प्रेरण क्या है?)
✅ Definition (परिभाषा)
English:
Induction is the process of producing EMF in a conductor due to change in magnetic flux.
Hindi:
जब किसी चालक में चुंबकीय फ्लक्स के परिवर्तन के कारण EMF उत्पन्न होता है, तो इसे प्रेरण कहते हैं।
👉 प्रेरण दो प्रकार की होती है:
✔ Self Induction
✔ Mutual Induction
🔷 Self Induction (स्व–प्रेरण)
✅ Self Induction Definition (स्व–प्रेरण की परिभाषा)
English:
Self induction is the phenomenon in which a changing current in a coil induces an EMF in the same coil.
Hindi:
जब किसी कुंडली में धारा के परिवर्तन से उसी कुंडली में EMF उत्पन्न होता है, तो इसे स्व–प्रेरण कहते हैं।
👉 सरल भाषा में:
Coil खुद ही अपने बदलाव का विरोध करती है।
⭐ यह ठीक Lenz’s Law का ही परिणाम है।
What is Website Designing
What is Twitter Marketing
🔷 How Self Induction Works? (स्व–प्रेरण कैसे कार्य करता है?)
मान लीजिए एक coil बैटरी से जुड़ी है।
👉 जब Current बढ़ता है:
- Magnetic field बढ़ता है
- Flux बदलता है
- Coil में EMF उत्पन्न होता है
- यह EMF current को बढ़ने से रोकता है
👉 जब Current घटता है:
- Magnetic field घटता है
- EMF उत्पन्न होता है
- यह current को बनाए रखने की कोशिश करता है
👉 यानी coil हमेशा change का विरोध करती है।
⭐ इसे Electrical Inertia (वैद्युत जड़त्व) भी कहते हैं।
🔷 Coefficient of Self Induction (स्व–प्रेरण गुणांक)
✅ Definition (परिभाषा)
किसी कुंडली में उत्पन्न EMF और धारा परिवर्तन की दर के अनुपात को Self Inductance कहते हैं।
✅ Formula (सूत्र)
[
E = – L \frac{dI}{dt}
]
जहाँ,
- L = Self Inductance
- dI/dt = धारा परिवर्तन की दर
👉 Negative sign → Lenz’s Law.
✅ Unit of Self Inductance (इकाई)
👉 Henry (हेनरी)
1 Henry:
यदि current 1 amp/sec की दर से बदले और 1 volt EMF बने।
🔷 Factors Affecting Self Inductance (स्व–प्रेरण को प्रभावित करने वाले कारक)
Self inductance निर्भर करता है:
✅ Turns की संख्या (N² के अनुपात में)
✅ Coil की लंबाई
✅ Cross-sectional area
✅ Core material (iron core → ज्यादा inductance)
👉 ज्यादा turns = ज्यादा inductance.
🔷 Energy Stored in an Inductor (इंडक्टर में संचित ऊर्जा)
जब coil में current बहता है, तो उसमें magnetic field बनता है और ऊर्जा stored होती है।
Formula:
[
U = \frac{1}{2} L I^2
]
👉 Exam में derivation भी पूछा जाता है।
🔷 Applications of Self Induction (स्व–प्रेरण के अनुप्रयोग)
✅ Choke coil – current control
✅ Electric circuits protection
✅ Transformers
✅ Motors
✅ Relays
👉 Fan regulators भी इसी principle पर काम करते हैं।
🔷 Mutual Induction (पारस्परिक प्रेरण)
✅ Mutual Induction Definition (पारस्परिक प्रेरण की परिभाषा)
English:
When changing current in one coil induces EMF in a nearby coil, it is called mutual induction.
Hindi:
जब एक कुंडली में धारा परिवर्तन से पास की दूसरी कुंडली में EMF उत्पन्न होता है, तो इसे पारस्परिक प्रेरण कहते हैं।
👉 आसान शब्दों में:
One coil helps induce EMF in another coil.
🔷 Working of Mutual Induction (पारस्परिक प्रेरण कैसे कार्य करता है?)
मान लें दो coils पास-पास रखी हैं।
👉 Coil 1 में current बदलता है
👉 Magnetic field बदलता है
👉 Flux coil 2 से गुजरता है
👉 Coil 2 में EMF उत्पन्न होता है
यह है mutual induction।
🔷 Coefficient of Mutual Induction (पारस्परिक प्रेरण गुणांक)
Formula:
[
E = – M \frac{dI}{dt}
]
जहाँ,
- M = Mutual Inductance
👉 Unit = Henry.
🔷 Factors Affecting Mutual Induction (पारस्परिक प्रेरण के कारक)
✅ दोनों coils की दूरी
✅ Turns की संख्या
✅ Core material
✅ Alignment of coils
👉 Iron core mutual induction को बहुत बढ़ा देता है।
🔷 Difference Between Self and Mutual Induction
(स्व-प्रेरण और पारस्परिक प्रेरण में अंतर)
| Self Induction | Mutual Induction |
| एक ही coil में EMF | दूसरी coil में EMF |
| Electrical inertia | Magnetic coupling |
| Single circuit | Two circuits |
⭐ Exam में 3–4 marks का question।
🔷 Applications of Mutual Induction (पारस्परिक प्रेरण के अनुप्रयोग)
✅ Transformer
सबसे महत्वपूर्ण example!
Voltage increase/decrease करने में उपयोग।
✅ Wireless Charging
Mobile charging में उपयोग।
✅ Induction Motor
Industrial machines में।
✅ Radio & TV
Signal transmission में।
🔷 Advantages (फायदे)
✅ Energy transfer बिना direct contact
✅ Safe power transmission
✅ Voltage control
✅ Efficient electrical systems
🔷 Disadvantages (नुकसान)
❌ Energy loss
❌ Leakage flux
❌ Heating
🔷 Numerical Example (संख्यात्मक उदाहरण)
यदि Self inductance = 2H
Current change = 4 A/sec
[
E = -2 \times 4 = -8V
]
👉 Magnitude = 8V.
🔷 Most Important Exam Points ⭐
✔ Self induction = Same coil
✔ Mutual induction = Two coils
✔ Unit = Henry
✔ Negative sign → Lenz law
✔ Transformer based question common
👉 UP Board Favorite!
🔷 Memory Trick 😄
👉 Self = Selfie (खुद)
👉 Mutual = Friends (दूसरा coil)
Students इसे जल्दी याद रखते हैं 🙂
🔷 Conclusion (निष्कर्ष)
Self और Mutual Induction आधुनिक electrical technology की रीढ़ हैं।
Transformer से लेकर wireless charging तक — हर जगह इनका उपयोग होता है।
यदि आप इन concepts को समझ लेते हैं, तो Physics का यह chapter आपके लिए scoring बन जाएगा।
📚 ऐसे ही आसान और exam-focused notes पढ़ते रहें — केवल gurugyanam.online पर।
❓ FAQs Self and Mutual Induction (स्व–प्रेरण एवं पारस्परिक प्रेरण)
Q1. Self induction क्या है?
Ans. एक ही coil में EMF उत्पन्न होना।
Q2. Mutual induction क्या है?
Ans. एक coil से दूसरी coil में EMF उत्पन्न होना।
Q3. Self inductance की SI unit?
Ans. Henry.
Q4. Mutual inductance की unit?
Ans. Henry.
Q5. Negative sign क्या दर्शाता है?
Ans. Lenz’s law (विरोध).
Q6. Self induction को क्या कहते हैं?
Ans. Electrical inertia.
Q7. Transformer किस पर आधारित है?
Ans. Mutual induction.
Q8. Inductor क्या है?
Ans. High inductance वाली coil.
Q9. Energy formula क्या है?
Ans. ½ LI².
Q10. Turns बढ़ाने पर क्या होगा?
Ans. Inductance बढ़ेगा।
Q11. Iron core क्यों उपयोग करते हैं?
Ans. Flux बढ़ाने के लिए।
Q12. Mutual induction किन पर निर्भर करता है?
Ans. Distance और turns पर।
Q13. Leakage flux क्या है?
Ans. जो दूसरी coil तक नहीं पहुँचता।
Q14. Self induction कहाँ उपयोग होता है?
Ans. Choke coil, circuits.
Q15. Wireless charging किस पर आधारित है?
Ans. Mutual induction.
Q16. EMF कब induce होता है?
Ans. जब current बदलता है।
Q17. Self vs Mutual का मुख्य अंतर?
Ans. एक coil vs दो coils।
Q18. Board exam में आता है?
Ans. हाँ, बहुत महत्वपूर्ण।
Q19. Fleming rule किस chapter में?
Ans. Electromagnetic induction.
Q20. Easy trick to remember?
Ans. Self = खुद, Mutual = दोनों।