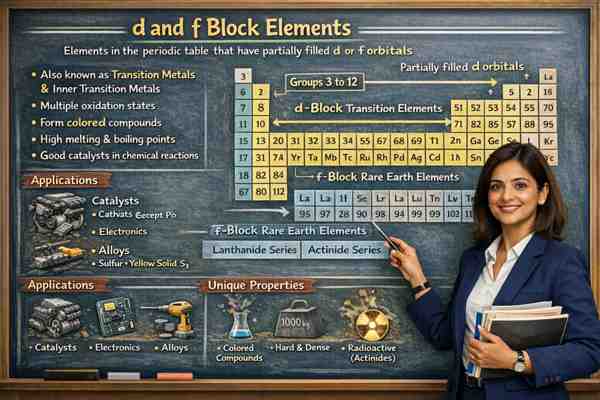
What are d and f Block Elements? | d और f ब्लॉक तत्व क्या हैं?
Periodic Table को चार blocks में बांटा गया है What are d and f Block Elements — s, p, d और f। इनमें से d और f block elements आधुनिक रसायन विज्ञान और उद्योग की रीढ़ (backbone) माने जाते हैं।
📌 परिभाषा (Definition):
वे तत्व जिनका अंतिम इलेक्ट्रॉन d या f orbital में प्रवेश करता है, d और f block elements कहलाते हैं।
👉 d-block elements को Transition Elements (संक्रमण तत्व) और f-block elements को Inner Transition Elements (आंतरिक संक्रमण तत्व) कहा जाता है।
UP Board Chemistry में यह chapter conceptual और scoring दोनों है।
👉 ऐसे ही सरल और exam-focused Chemistry notes पढ़ने के लिए विजिट करें:
✅ gurugyanam.online
What is Online Marketing
What is Mobile Marketing
What are d and f Block Elements
Position in Periodic Table | आवर्त सारणी में स्थान
✅ d-Block:
- Group → 3 से 12
- Middle of periodic table
✅ f-Block:
- Table के नीचे अलग से दिखाए जाते हैं
- Period → 6 और 7
👉 इन्हें नीचे इसलिए रखा गया है ताकि table compact रहे।
What are d and f Block Elements
Electronic Configuration | इलेक्ट्रॉनिक विन्यास
✅ d-Block:
👉 (n-1)d¹–¹⁰ ns¹–²
Example:
Fe → [Ar] 3d⁶ 4s²
✅ f-Block:
👉 (n-2)f¹–¹⁴ (n-1)d⁰–¹ ns²
Example:
Cerium → [Xe] 4f¹ 5d¹ 6s²
📌 Exam Tip:
d-block → second last shell
f-block → third last shell
What are Transition Elements? | संक्रमण तत्व क्या हैं?
वे d-block elements जिनमें partially filled d-orbitals होते हैं, transition elements कहलाते हैं।
👉 Example: Iron (Fe), Copper (Cu), Nickel (Ni)
What are d and f Block Elements
General Characteristics of d-Block Elements | d-ब्लॉक तत्वों की सामान्य विशेषताएँ
⭐ High melting & boiling points
⭐ Good conductors
⭐ Metallic nature
⭐ Variable oxidation states
⭐ Colored compounds
⭐ Magnetic behavior
👉 इन्हें “typical metals” भी कहा जाता है।
Variable Oxidation States | परिवर्ती ऑक्सीकरण अवस्थाएँ
Transition metals कई oxidation states दिखाते हैं क्योंकि:
👉 ns और (n-1)d electrons दोनों bonding में भाग लेते हैं।
Examples:
✔ Iron → +2, +3
✔ Copper → +1, +2
✔ Manganese → +2 to +7
📌 Exam favorite topic!
Colored Compounds | रंगीन यौगिक
Transition elements के compounds अक्सर colored होते हैं।
👉 Reason: d–d electronic transitions
Examples:
✔ CuSO₄ → Blue
✔ KMnO₄ → Purple
✔ K₂Cr₂O₇ → Orange
📌 Direct question बनता है।
What are d and f Block Elements
Magnetic Properties | चुंबकीय गुण
Transition metals paramagnetic होते हैं।
👉 Unpaired electrons के कारण।
Types:
✔ Diamagnetic → No unpaired electrons
✔ Paramagnetic → Unpaired electrons
✔ Ferromagnetic → Strong magnetism
Example: Iron, Cobalt, Nickel
What are d and f Block Elements
Catalytic Properties | उत्प्रेरक गुण
Transition metals excellent catalysts होते हैं।
Examples:
✔ Iron → Haber Process
✔ Vanadium oxide → Contact Process
✔ Nickel → Hydrogenation
👉 Industrial chemistry का आधार।
Formation of Complex Compounds | समिश्र यौगिक बनाना
Transition metals ligands के साथ complex बनाते हैं।
Example:
[Cu(NH₃)₄]²⁺
📌 Coordination chemistry का base।
Alloy Formation | मिश्रधातु निर्माण
Transition metals आसानी से alloys बनाते हैं।
Examples:
✔ Steel (Fe + C)
✔ Brass (Cu + Zn)
✔ Bronze (Cu + Sn)
👉 Stronger materials।
What are f-Block Elements? | f-ब्लॉक तत्व क्या हैं?
f-block elements को Inner Transition Elements कहा जाता है।
दो series होती हैं:
👉 Lanthanides (Lanthanum series)
👉 Actinides (Actinium series)
Lanthanides | लैंथेनाइड्स
Atomic numbers: 57–71
👉 Rare earth elements भी कहलाते हैं।
Properties:
✔ Soft metals
✔ High reactivity
✔ Mostly +3 oxidation state
Lanthanide Contraction | लैंथेनाइड संकुचन**
Atomic size धीरे-धीरे घटता है।
👉 Reason: Poor shielding of f-electrons।
📌 Very important concept!
Uses:
✔ Magnets
✔ Camera lenses
✔ Hybrid cars
✔ Lasers
Actinides | एक्टिनाइड्स
Atomic numbers: 89–103
👉 Mostly radioactive।
Properties:
✔ Multiple oxidation states
✔ Highly reactive
✔ Radioactive nature
Important Elements:
Uranium (U)
✔ Nuclear fuel
Thorium (Th)
✔ Future nuclear energy
📌 Competitive exams में important।
Difference Between d and f Block | d और f ब्लॉक में अंतर
| Basis | d-block | f-block |
| Position | Middle | Bottom |
| Orbitals | d | f |
| Oxidation states | Variable | Mostly +3 |
| Radioactivity | Rare | Common |
Industrial Importance | औद्योगिक महत्व
✔ Construction metals
✔ Electrical wiring
✔ Batteries
✔ Nuclear reactors
✔ Electronics
👉 Modern civilization इन पर निर्भर है।
Biological Importance | जैविक महत्व
✔ Iron → Hemoglobin
✔ Zinc → Enzymes
✔ Copper → Metabolism
👉 Life processes में essential।
Environmental Impact | पर्यावरणीय प्रभाव
✔ Mining pollution
✔ Radioactive waste
✔ Heavy metal toxicity
👉 Sustainable use जरूरी।
Exam Important Points | परीक्षा उपयोगी तथ्य
⭐ Transition elements → Variable oxidation
⭐ Colored compounds
⭐ Lanthanide contraction
⭐ Actinides radioactive
⭐ Excellent catalysts
👉 Direct questions बनते हैं।
Common Mistakes Students Make | छात्रों की सामान्य गलतियाँ
❌ d और f block confuse करना
❌ Lanthanide contraction भूलना
❌ Oxidation states याद न रखना
👉 Concept clarity जरूरी।
Why Students Must Study d and f Block? | यह टॉपिक क्यों जरूरी है?
✔ Board exams में repeated
✔ Concept-based
✔ Easy scoring
✔ Industrial relevance
👉 Smart preparation का हिस्सा।
Future of d and f Block Elements | भविष्य
✔ Green energy
✔ Electric vehicles
✔ Advanced magnets
✔ Nuclear power
👉 Technology का future इन्हीं पर निर्भर है।
Conclusion | निष्कर्ष
d और f block elements chemistry के सबसे महत्वपूर्ण topics में से हैं। Transition metals से लेकर radioactive actinides तक — इनका योगदान industry, medicine और technology में अत्यंत बड़ा है।
UP Board students को oxidation states, colored compounds और lanthanide contraction जरूर याद रखने चाहिए। यह chapter conceptual और scoring दोनों है।
👉 ऐसे ही सरल और exam-focused Chemistry notes पढ़ने के लिए विजिट करें:
✅ gurugyanam.online
FAQs – What are d and f Block Elements (d और f ब्लॉक तत्व)
Q1. d-block elements क्या हैं?
Ans. जिनका last electron d orbital में जाता है।
Q2. f-block elements क्या हैं?
Ans. Last electron f orbital में।
Q3. Transition elements क्या हैं?
Ans. Partially filled d orbitals वाले।
Q4. Inner transition elements?
Ans. Lanthanides और Actinides।
Q5. Lanthanide contraction क्या है?
Ans. Atomic size decrease।
Q6. Colored compounds क्यों?
Ans. d–d transition।
Q7. Variable oxidation क्यों?
Ans. ns और d electrons।
Q8. Catalyst example?
Ans. Iron।
Q9. Alloy क्या है?
Ans. Metal mixture।
Q10. Actinides कैसे हैं?
Ans. Radioactive।
Q11. Uranium use?
Ans. Nuclear fuel।
Q12. Iron biological role?
Ans. Hemoglobin।
Q13. Paramagnetic क्यों?
Ans. Unpaired electrons।
Q14. Rare earth elements कौन?
Ans. Lanthanides।
Q15. Steel क्या है?
Ans. Iron alloy।
Q16. Oxidation state common?
Ans. +2, +3।
Q17. Table में position?
Ans. Middle & bottom।
Q18. Easy chapter है?
Ans. हाँ।
Q19. Industrial importance?
Ans. High।
Q 20. Future tech dependent?
Ans. हाँ।
👉 ऐसे ही सरल और exam-focused Chemistry notes पढ़ने के लिए विजिट करें:
✅ gurugyanam.online