General Principles & Processes of Metallurgy (धातुकर्म के सामान्य सिद्धांत एवं प्रक्रियाएँ) क्या हैं? Ore, concentration, roasting, calcination, reduction, refining, Ellingham diagram, flux, slag और परीक्षा उपयोगी 20 FAQs को आसान हिंदी में पढ़ें – केवल gurugyanam.online पर।
What is Metallurgy? | धातुकर्म क्या है?
Chemistry में General Principles & Processes of Metallurgy (धातुकर्म) वह प्रक्रिया है जिसके द्वारा हम पृथ्वी की सतह से प्राप्त अयस्क (Ore) से शुद्ध धातु (Pure Metal) निकालते हैं।
👉 सरल शब्दों में:
अयस्क से धातु निकालने की विज्ञान और तकनीक = धातुकर्म
आज की modern civilization — buildings, vehicles, machines, electronics — सभी धातुओं पर निर्भर हैं। इसलिए metallurgy को industrial chemistry की backbone कहा जाता है।
📌 परिभाषा (Definition):
अयस्क से धातु के निष्कर्षण (extraction) तथा शुद्धिकरण (refining) की प्रक्रिया को धातुकर्म कहते हैं।
UP Board और competitive exams में यह chapter बेहद scoring माना जाता है।
What is Online Reputation Management
General Principles & Processes of Metallurgy
Occurrence of Metals | प्रकृति में धातुओं की उपस्थिति
धातुएँ प्रकृति में दो रूपों में मिलती हैं:
✅ 1. Native State (मूल अवस्था)
जब धातु free form में मिलती है।
Examples:
✔ Gold (Au)
✔ Silver (Ag)
✔ Platinum (Pt)
👉 ये कम reactive होती हैं।
General Principles & Processes of Metallurgy
✅ 2. Combined State (संयोजित अवस्था)
अधिकतर धातुएँ compounds के रूप में मिलती हैं।
Examples:
✔ Oxides
✔ Sulphides
✔ Carbonates
👉 इन्हें निकालने के लिए metallurgy जरूरी है।
Important Terms in Metallurgy | धातुकर्म की महत्वपूर्ण शब्दावली
✅ Ore (अयस्क)
ऐसा खनिज जिससे धातु economically निकाली जा सके।
👉 Example: Bauxite → Aluminium
✅ Mineral (खनिज)
प्राकृतिक रूप से पाए जाने वाले compounds।
📌 हर mineral ore नहीं होता।
✅ Gangue (अशुद्धियाँ)
Ore में मौजूद मिट्टी, रेत, पत्थर आदि unwanted पदार्थ।
✅ Flux (फ्लक्स)
Gangue हटाने के लिए मिलाया जाने वाला पदार्थ।
✅ Slag (स्लैग)
Flux + Gangue → Slag
👉 यह molten waste होता है।
📌 Exam Tip:
Flux removes gangue → forms slag
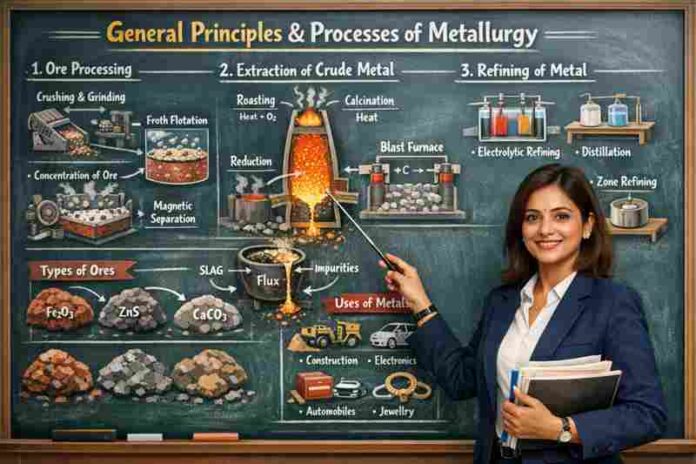
Steps of Metallurgy | धातुकर्म के चरण
Metal extraction मुख्यतः तीन steps में होता है:
👉 1. Concentration of Ore
👉 2. Extraction of Metal
👉 3. Refining (Purification)
अब इन्हें विस्तार से समझते हैं।
Concentration of Ore (अयस्क का सांद्रण)
इस प्रक्रिया में gangue हटाकर ore को शुद्ध किया जाता है।
Methods:
✅ 1. Hydraulic Washing (गुरुत्वीय पृथक्करण)
Density difference पर आधारित।
👉 Heavy ore नीचे बैठता है।
General Principles & Processes of Metallurgy
✅ 2. Magnetic Separation
Magnetic properties का उपयोग।
✔ Magnetic ore → Magnet से attach
✔ Non-magnetic → अलग
✅ 3. Froth Flotation (फ्रॉथ फ्लोटेशन)
Sulphide ores के लिए।
👉 Oil + water मिलाने पर ore foam में ऊपर आ जाता है।
📌 Important for exams!
✅ 4. Leaching (लीचिंग)
Chemical solution से metal dissolve।
👉 Example:
Bauxite + NaOH → Aluminium extraction
Extraction of Metal | धातु का निष्कर्षण
अब concentrated ore से metal निकाला जाता है।
✅ Calcination (कैल्सिनेशन)
Ore को limited या बिना oxygen के गर्म किया जाता है।
👉 Carbonates और hydrated ores के लिए।
Example:
ZnCO₃ → ZnO + CO₂
📌 Removes moisture and volatile impurities.
✅ Roasting (रोस्टिंग)
Sulphide ore को excess oxygen में गर्म किया जाता है।
👉 Sulphide → Oxide
Example:
2ZnS + 3O₂ → 2ZnO + 2SO₂
📌 Exam favorite reaction!
✅ Reduction (अपचयन)
Metal oxide से oxygen हटाकर pure metal प्राप्त किया जाता है।
Methods:
✔ Carbon Reduction
Fe₂O₃ + 3C → 2Fe + 3CO
✔ Electrolytic Reduction
Highly reactive metals के लिए।
👉 Example: Aluminium, Sodium
📌 Electrolysis is very important!
Ellingham Diagram | एलिंघम आरेख
यह diagram बताता है कि कौन सा metal oxide आसानी से reduce होगा।
👉 Lower line → More stable oxide
👉 Higher temperature → Easier reduction
📌 Competitive exams में अक्सर पूछा जाता है।
Refining of Metals | धातुओं का शुद्धिकरण
Extraction के बाद metal पूरी तरह pure नहीं होता।
इसलिए refining जरूरी है।
Methods of Refining:
✅ 1. Distillation
Low boiling metals के लिए।
👉 Zinc, Mercury
✅ 2. Liquation
Low melting metals।
👉 Tin, Lead
✅ 3. Electrolytic Refining (सबसे महत्वपूर्ण)
Impure metal → Anode
Pure metal → Cathode
👉 Example: Copper refining
📌 Exam Tip:
Anode mud contains precious metals.
Thermodynamic Principles | ऊष्मागतिक सिद्धांत
Metal extraction feasibility Gibbs free energy से तय होती है।
👉 Negative ΔG → Reaction possible
यह concept Ellingham diagram से जुड़ा है।
General Principles & Processes of Metallurgy
Reactivity Series and Metallurgy | अभिक्रियाशीलता श्रेणी
Metals को तीन भागों में बांटा जाता है:
✅ Highly Reactive
Na, K, Ca → Electrolysis
✅ Moderately Reactive
Zn, Fe → Carbon reduction
✅ Low Reactive
Au, Ag → Native state
📌 यह classification exam में जरूर आता है।
Environmental Impact | पर्यावरणीय प्रभाव
Metallurgy से pollution हो सकता है।
❌ SO₂ gas
❌ Water contamination
❌ Land degradation
👉 Modern industries eco-friendly methods अपना रही हैं।
Applications of Metallurgy | धातुकर्म के उपयोग
✔ Construction
✔ Automobile
✔ Electronics
✔ Aerospace
✔ Medical equipment
👉 Metallurgy = Industrial development।
Advantages | फायदे
✔ Pure metals production
✔ Strong alloys
✔ Economic growth
✔ Infrastructure development
Disadvantages | नुकसान
❌ Pollution
❌ Energy consumption
❌ Mining hazards
Exam Important Points | परीक्षा उपयोगी तथ्य
⭐ Ore vs Mineral
⭐ Flux + Gangue = Slag
⭐ Roasting vs Calcination
⭐ Electrolytic refining
⭐ Ellingham diagram
⭐ Froth flotation
👉 ये topics बार-बार पूछे जाते हैं।
Why Metallurgy is Important? | धातुकर्म क्यों महत्वपूर्ण है?
कल्पना करें अगर metallurgy न हो:
❌ Buildings नहीं
❌ Vehicles नहीं
❌ Machines नहीं
❌ Technology नहीं
👉 Modern life असंभव हो जाएगी।
Conclusion | निष्कर्ष
General Principles & Processes of Metallurgy chemistry का एक foundational chapter है। यह न केवल exams के लिए महत्वपूर्ण है बल्कि industrial world को समझने के लिए भी जरूरी है।
UP Board students को extraction steps, refining methods और reactions जरूर याद करनी चाहिए। यह chapter conceptual और scoring दोनों है।
👉 ऐसे ही सरल और exam-focused Chemistry notes पढ़ने के लिए विजिट करें:
✅ gurugyanam.online
FAQs – General Principles & Processes of Metallurgy (धातुकर्म के सामान्य सिद्धांत एवं प्रक्रियाएँ)
Q1. Metallurgy क्या है?
Ans. अयस्क से धातु निकालने की प्रक्रिया।
Q2. Ore क्या है?
Ans. धातु निकालने योग्य खनिज।
Q3. Gangue क्या है?
अशुद्धियाँ।
Q4. Flux क्या करता है?
Ans. Gangue हटाता है।
Q5. Slag क्या है?
Ans. Flux + gangue।
Q6. Calcination क्या है?
Ans. Limited oxygen में heating।
Q 7. Roasting क्या है?
Ans. Excess oxygen में heating।
Q 8. Reduction क्या है?
Ans. Oxygen हटाना।
Q9. Froth flotation किसके लिए?
Ans. Sulphide ores।
Q10. Magnetic separation किस पर आधारित है?
Ans. Magnetic property।
Q11. Leaching क्या है?
Ans. Chemical dissolution।
Q12. Electrolysis किसके लिए?
Ans. Highly reactive metals।
Q13. Ellingham diagram क्या दिखाता है?
Ans. Reduction feasibility।
Q14. Electrolytic refining example?
Ans. Copper।
Q15. Distillation किसके लिए?
Ans. Low boiling metals।
Q 16. Liquation किसके लिए?
Ans. Low melting metals।
Q 17. ΔG negative का मतलब?
Ans. Reaction possible।
Q18. Native metals example?
Ans. Gold।
Q19. Metallurgy क्यों जरूरी है?
Ans. Industrial development।
Q20. Most important exam topic?
Ans. Roasting vs Calcination।
👉 ऐसे ही सरल और exam-focused Chemistry notes पढ़ने के लिए विजिट करें:
✅ gurugyanam.online